在使用串口接受字符串时,可以使用空闲中断(IDLEIE置1,即可使能空闲中断),这样在接收完一个字符串,进入空闲状态时(IDLE置1)便会激发一个空闲中断。在中断处理函数,我们可以解析这个字符串。
需要注意的是,IDLE标志位需要软件清零,否则由于会不断进入中断,而使正常程序无法运行。当再次收到数据时(即RXNE再次置1),等到空闲便会重新进入中断。
在STM32F4中,IDLE标志位清零的过程是:先读SR,再读DR寄存器。
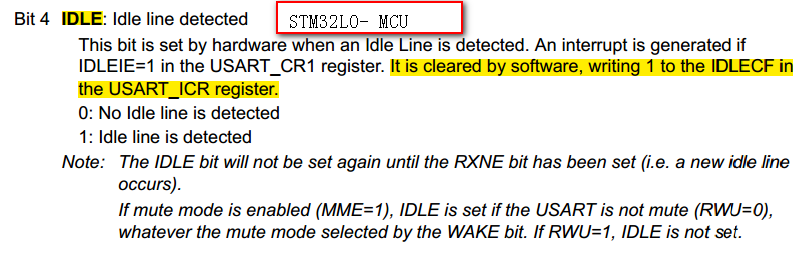
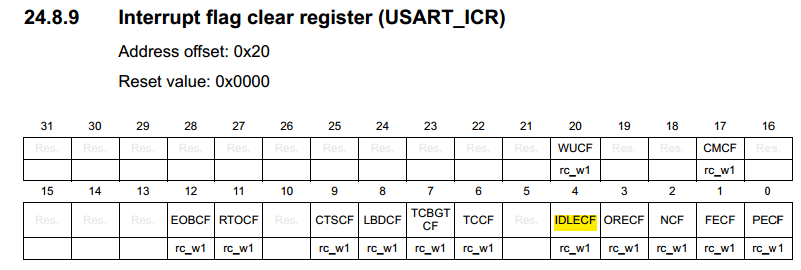
而在STM32L0中, idle标志清除的过程是:对ICR寄存器的IDLECF位写1
切记使用正确的方式清零IDLE标志位,不同系列的清零方式有可能不同!在移植时需要注意,我将F4的程序移植到L0上时,忽略了这个问题找了很久才找到问题根源。

转自: Linux社区